How business intelligence in manufacturing streamlines data-driven decisions – and why you can’t ignore it
March 12, 2025Manufacturing is no longer just about machines and production lines – it’s about data. Manufacturers who successfully use data collection through IoT solutions lead the market while behind competitors fall into delay. The manufacturing sector transforms its operations through business intelligence (BI), which creates instant insights from complex datasets to allow companies to track equipment faults, enhance workflow efficiency, and predict market trends. Mechanisms powered by business intelligence enable companies to base their strategic decisions on actual data, which leads to efficiency improvement, cost reduction, and productivity enhancement. The rising market competition demands the implementation of BI across manufacturing facilities because it ensures prolonged business success. So, how does business intelligence in manufacturing streamline data-driven decisions? Let’s break it down.
The game-changing role of business intelligence in manufacturing
Businesses can utilize business intelligence (BI) to exchange raw data into actionable insights, analyze substantial datasets from supply chains and production lines to client associations, and make informed decisions. BI allows companies to discover inefficiencies, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and make the most effective use of resources, which reduces operational costs and enhances product quality. In addition to real-time data visualization and predictive analytics, manufacturers can anticipate disruptions, optimize maintenance schedules, simplify production processes, and thereby improve agility and responsiveness in stiff competition.
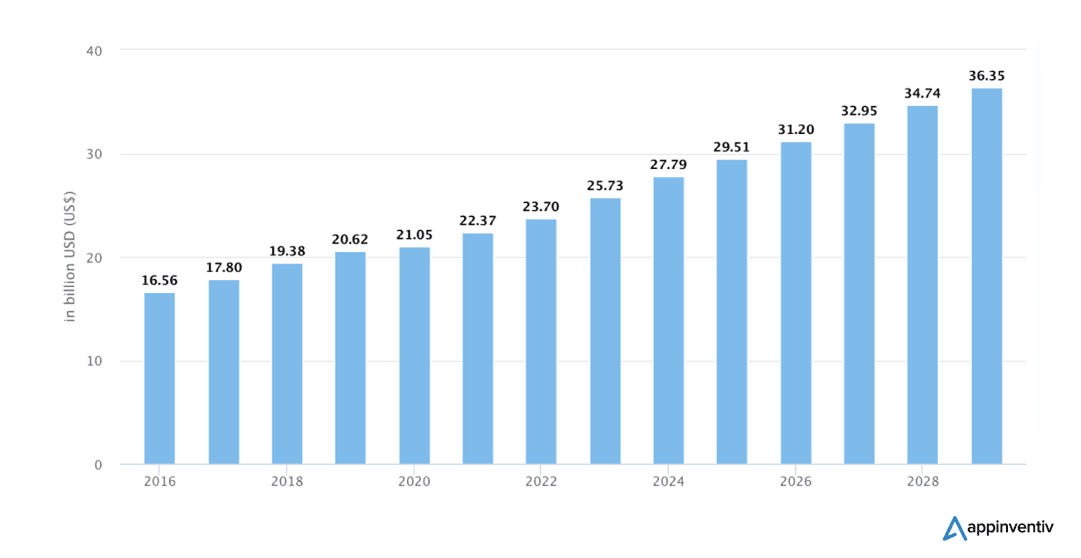
The manufacturing sector's growing reliance on data analytics to handle the complexities brought about by Industry 5.0 technologies is the main driver of the BI software market's rapid expansion, which is expected to reach over $36.35 billion by 2029, according to Statista. Manufacturers adopt advanced systems like IoT and AI, and the demand for strong BI tools keeps rising as these solutions enable organizations to harness big data effectively. Moreover, integrating BI with other technologies improves departmental collaboration and communication - all stakeholders can use data for strategic planning and operational excellence. This interconnected relationship between BI software and the manufacturing sector highlights the critical role that data-driven strategies play in attaining sustainable growth.
Must-have BI integrations that supercharge manufacturing efficiency
Manufacturers rely on key business intelligence (BI) integrations to unify systems like ERP, MES, and CRM – this ensures seamless data flow and comprehensive operational insights. Let’s consider how BI enhances various aspects of manufacturing:
- Seamless ERP connections – integrating BI with ERP solutions provides real-time visibility into financials, inventory, and production schedules. It enables data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Smarter supply chains with data insights – BI-driven supply chain integration improves demand forecasting, inventory control, and supplier performance tracking, resulting in streamlined logistics and reduced costs.
- IoT-powered real-time monitoring – connecting BI with IoT devices allows manufacturers to monitor equipment performance, track production metrics, and implement predictive maintenance. Results of investing in IoT: minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
- AI-driven quality control – through quality management tools, manufacturers can analyze defect trends, detect anomalies, and take proactive measures to maintain high product standards.
- Next-level CRM for customer-centric manufacturing – BI-powered CRM integration offers deep insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and market demands. It helps manufacturers refine their marketing strategies and product offerings.
- Manufacturing execution systems (MES) for precision and performance – linking BI with MES allows manufacturers to track work in progress, analyze production data, and optimize workflows.
- Enterprise asset management (EAM) for maximized ROI – BI integration with EAM systems enhances asset tracking, maintenance scheduling, and resource utilization, leading to improved equipment reliability and minimized downtime.
How business intelligence transforms manufacturing efficiency
Business Intelligence reshapes the manufacturing industry by turning vast data into actionable insights. BI enables manufacturers to work smarter, reduce costs, and stay competitive in an evolving market.
- Smarter quality control. Production quality monitoring through BI systems takes place in real time to help manufacturers discover defects quickly and reduce rework expenses. Quality metrics and IoT dashboards enable companies to ensure products meet regulatory demands and customer expectations at all times. This approach boosts brand reputation and customer loyalty in the long term
- Optimized supply chain management. Supply chain management that relies on data brings complete transparency to procurement, inventory, and supplier performance. Through lead time analysis, manufacturers can analyze lead times, anticipate demand fluctuations, and improve coordination with suppliers, which cuts costs and accelerates product shipment times. Businesses can quickly adapt to market shifts and changing customer preferences through improved organizational speed.
- Data-driven decision-making. Companies that use Business Intelligence gain access to current operational data alongside market trends and production efficiencies, which enables them to move past intuition-based choices. Through data analytics, leaders acquire the power to make strategic decisions that boost profitability combined with growth strategies and minimize the need to base decisions on outdated reports or guesswork.
- Cost reduction and efficiency gains. BI identifies inefficiencies and optimizes resource allocation, this way helping manufacturers reduce operational expenses. From better inventory management to streamlined workflows, BI-driven insights lower costs associated with waste, delays, and excess stock. Also, improved machine utilization and labor efficiency contribute to higher productivity without added expenses.
Use cases of predictive maintenance in manufacturing
Predictive maintenance transforms manufacturing by leveraging data analytics to anticipate equipment failures before they occur. Using sensors, IoT devices, and BI tools, manufacturers can optimize maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of machinery. Here are key use cases of predictive maintenance in manufacturing:
1. Automotive manufacturing – minimizing production line disruptions
The IoT-powered predictive maintenance solution enables continuous observation of vital industrial machines, which includes robotic arms and conveyor systems, to identify and detect irregularities in motor operations and temperature variations. The monitoring system identifies equipment failures at an early stage; thus, manufacturers can prevent halted production and minimize expenses from equipment breakdowns.
2. Aerospace – ensuring aircraft engine reliability
General Electric (GE) utilizes predictive maintenance technology for real-time aircraft engine monitoring. By analyzing temperature, pressure, and vibration data, potential failures can be found early, allowing proactive repair processes to begin. These processes lead to increased safety measures and decreased maintenance expenses while maintaining continuous aircraft operations.
3. Food & beverage industry – preventing equipment failures
Predictive maintenance monitors refrigeration units, conveyor belts, and mixing equipment in food processing facilities. The analysis of sensors helps organizations avoid equipment failures, which could result in production schedule disruptions or hazardous situations related to contamination. The monitoring system enables full adherence to food security regulations.
4. Heavy machinery – optimizing asset utilization
The manufacturing industry uses predictive services on heavy equipment devices such as mining and construction machines to track engine functions, hydraulic systems, and fuel parameters. Remote area breakdowns become avoidable because such systems help reduce maintenance expenses and increase operational availability.
Best practices for making business intelligence work for your factory floor
Successfully adopting Business Intelligence in manufacturing necessitates careful planning and execution. Let’s consider key best practices to ensure a smooth and effective implementation:
- Define clear objectives. You should begin by selecting BI objectives that support their company strategy to enhance operation efficiency or product quality. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that will serve as success metrics while keeping stakeholders involved for alignment purposes. Review your performance objectives periodically to refine those that stem from existing data.
- Engage key stakeholders. Start the BI project by incorporating department leaders and end-users early to gather insights on their data needs. Organize workshops that unite IT and business departments to improve mutual understanding of BI's value. Create a feedback loop to improve the system continuously.
- Prioritize data quality. The effectiveness of BI depends on accurate data. Implement strong data governance policies, conduct regular audits, and use data-cleaning tools to maintain accuracy. Encourage employees to take ownership of data integrity.
- Choose the right BI tools. Select BI solutions that are user-friendly, scalable, and compatible with existing systems. Ensure the tools offer strong integration capabilities and reliable vendor support.
- Start small, scale gradually. Begin with a pilot project in one department to demonstrate BI’s value and troubleshoot challenges. Expand implementation based on lessons learned, reducing risks and ensuring long-term success.
The bottom line: why business intelligence is no longer optional for manufacturers
The manufacturing industry experiences a revolutionary change through Business Intelligence, which converts large data volumes into actionable insights that lead to operational improvements, financial savings, and strategic business decisions. Manufacturers use BI to obtain essential insights that drive enterprise-wide efficiency and supply chain optimization, which enables them to succeed in the current data-driven market. Real-time operational monitoring made possible by BI system integration with ERP, MES, and IoT devices allows users to foresee production interruptions, boost productivity, and minimize operational costs.
The advancing Industry 5.0 technologies will create expanding requirements for sophisticated BI solutions. Organizations that implement strategic data analysis methods with strong attention to quality data collection, stakeholder involvement, and BI system scalability will achieve maximum benefits from their analytical data. Organizations must embrace data-driven culture development because it stands essential for their present innovation alongside operation optimization and sustainable business growth. To remain competitive, manufacturers must embrace BI as a critical tool for improving decision-making, optimizing resources, and ensuring long-term success in an increasingly digital and connected industrial landscape.




