Integration of AI and IoT: Benefits and Challenges
December 24, 2024The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating a new technological ecosystem — AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things). The combination of these two technologies allows expanding the functionality of classic IoT devices, transforming them from simple data collectors into autonomous systems that can analyze, learn, and make decisions in real time. The creation of AIoT has opened up new ways to develop automation of IoT infrastructures with the ability to apply them in various industries.
The main advantage of AIoT is that IoT devices can collect information, process it using AI, make predictions based on it, and initiate actions without human intervention. Thanks to edge computing (computing at the network periphery), this integration also reduces delays and increases the reliability of such systems.
However, with all the benefits of AIoT, some challenges are related to the privacy and security of the data being processed. These integration aspects are key to identifying all the limitations and opportunities created by the combination of AI and IoT, and we will discuss them in this article.
The main components of AIoT and their role
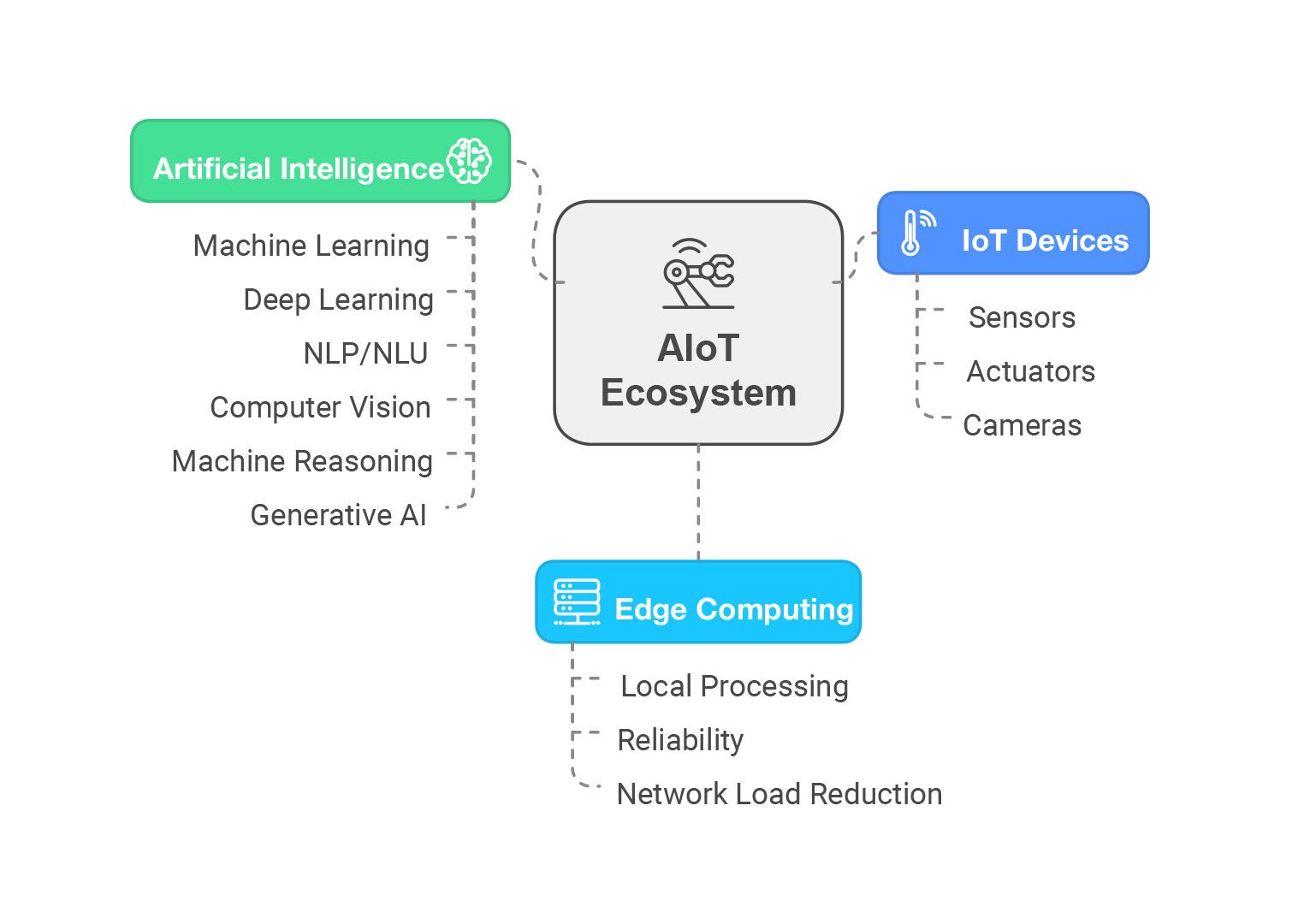
The AIoT (Internet of Things combined with artificial intelligence) functions thanks to three main components: IoT devices, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and edge computing. Individually, each of these components is not as strong as their joint work, which creates a perfectly balanced synergy between them.
IoT devices
IoT devices include sensors, actuators, cameras, and other devices that collect information from and interact with the environment. IoT devices are physical embodiments of virtual platforms that manage and monitor smart systems. Sensors can monitor air parameters, actuators (electric motor, hydraulic system, and pneumatic system) can physically affect the real world, and cameras can capture and analyze objects and people.
All of these devices generate large amounts of data that can be described and structured for further use. For example, video surveillance cameras can collect information about car traffic to reduce congestion, and smart sensors can protect and report a water leak.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence can be used to process data coming from IoT devices and use it to make predictions, make decisions, and initiate actions. Artificial intelligence works with data more efficiently than humans, with fewer errors and at a higher speed by automating processes, and with the help of machine learning, AI can improve its skills in similar scenarios. Thus, AI helps IoT devices to act autonomously and perform tasks that previously required human intervention.
Existing artificial intelligence (AI) is just a collection of technologies and algorithms. It consists of technologies such as machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), natural language processing and understanding (NLP/NLU), computer vision (CV), machine reasoning (MR), and generative AI (GenAI).
Most of the available AIs are built on machine learning (ML). They allow computers to analyze massive amounts of data and then apply these analyses to make predictions, classify data, recognize objects, and automate processes.
Edge Computing
Edge computing (or computing at the network periphery) allows data to be processed at the point of generation/collection, without the need to transfer data to the cloud. There are also solutions in which the data generated by IoT devices is processed by the devices themselves, but such solutions require more power from the devices.
This principle of building computing systems is especially useful in scenarios where a reaction with minimal delay is required. For example, when integrating such a system into a smart building, all calculations and emergency responses will be processed locally, which minimizes delays, improves reliability, and reduces network load.
Benefits of integrating AI and IoT
The ability of AIoT to automate routine tasks performed by humans helps to optimize workflows and increase resource efficiency. It improves system performance, reduces labor costs, and helps to execute operations faster. We are going to look at 5 key benefits of AI and IoT integration, which in turn affect both economic and technical aspects of automation.
1. Improving operational efficiency
The main advantage of AIoT is the ability to increase operational efficiency by automating routine tasks. Repetitive operations, such as IoT energy management, can be fully transferred to the AIoT system. This allows a company or production to allocate human resources more efficiently between different stages of business processes.
2. Predictive maintenance
AIoT integration will provide tools for predictive maintenance, which helps to avoid unplanned equipment repairs. By monitoring equipment parameters in real time and analyzing its performance using AI, an automated system can predict when maintenance will be required. This helps protect against unplanned repairs and downtime, helping businesses avoid additional costs and minimize downtime.
3. Improved decision-making
AIoT makes it possible to make all decisions regarding the regulation of processes based on relevant data collected in real time. The availability of always up-to-date data makes it possible to adjust to dynamic changes and solve problems quickly. For example, analyzing the flow of people in a large shopping center will allow you to analyze the most popular routes to build evacuation routes and identify points of interest. As a result, the company will make informed decisions, reducing the risks associated with operational processes.
4. Optimization of energy consumption
AIoT can optimize energy use by monitoring energy consumption around the clock. AIoT integrated into buildings with smart home systems analyzes data from motion sensors and video surveillance cameras to effectively adjust climate control and lighting systems. This not only improves the comfort of staying in the building but also leads to significant cost savings for businesses by optimizing energy-intensive operations.
5. Improving customer experience
Integration of AI with IoT helps brands to personalize their services. Collecting and analyzing data on customers, their preferences, and behavioral patterns allows the creation of more relevant offers and speeds up the response to customer needs. This personalized approach improves the customer experience and positively affects customer perception of the brand.
Challenges of integrating AI and IoT
No matter how ideal the synergy of these technologies may seem, their global adoption has many limitations. From legislative to technical incompatibility with old systems, all these limitations significantly slow down the global application of these technologies. Let's consider 5 critical challenges that have the greatest impact on the adoption of AIoT technology.
Data privacy and security
To operate efficiently, AIoT systems need to process significant amounts of personal and commercially sensitive data. Misuse of this sensitive data threatens the safety of people and business secrets. Cybersecurity and the protection of this data from unauthorized access is becoming a crucial task, as its theft can have serious consequences for companies and their customers.
Interoperability of devices and standards
The AIoT ecosystem cannot exist in isolation, it requires constant communication with a variety of devices and IoT platforms. Since different generations and manufacturers have their own standards and communication protocols for devices, this creates an interoperability problem within the entire ecosystem. For example, if devices from different manufacturers are not properly integrated into a smart city system, any incompatibility can disrupt the entire system and create cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Explainability and transparency of algorithms
Today, AI algorithms are not yet perfect enough to fully rely on them for critical aspects of our lives, such as medicine or strategic communications. Lack of clarity about AI solutions in the medical field can lead to user distrust of the technology. For example, if medical devices provide doctors with treatment recommendations without clear explanations, this can lead to errors that affect the patient's health.
Power consumption and limited computing power
AIoT devices require significant computing power to operate. Fast decision-making and all data operations will directly depend on the resources of the devices or their data center. A new milestone in the development of ARM processors has created new hope for powerful and energy-efficient solutions, but the technology still needs to be optimized. For example, industrial sensors are subject to rather stringent requirements for power, reliability, and battery life, so testing new products in this and similar industries is difficult.
Protection against algorithm manipulation (cybersecurity threats)
AIoT systems also depend on the quality of input data. Distortions or intentional interference (in the case of cyberattacks) in the input data flow can disrupt the entire ecosystem. For example, in transportation systems, minor changes in road signage data can lead autopilot vehicles off the correct route, which can create an emergency.
Prospects for AIoT application in various industries
As AIoT evolves, it will become the driving technology that will change the world, just like IoT did. Its capabilities allow it to be used in all possible industries, from medicine to IoT smart building solutions. We can highlight the important role of this technology in the following industries:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, AIoT will improve patient monitoring by detecting even minor deviations in indicators. This allows for timely interventions and prevention.
- Agriculture: Integration of AIoT will help automate processes in agriculture, such as irrigation, soil control, and weather monitoring.
- Transportation: With real-time monitoring, transportation systems can easily adapt to changes in traffic flow and support autonomous navigation.
- Smart buildings: In commercial and residential buildings, AIoT will provide automatic control of energy consumption and other critical networks, reducing costs and increasing comfort.
Integrating AI and IoT creates AIoT technology, which is an example of perfect synergy in automation and monitoring.
So far, AIoT integration has been accompanied by significant challenges, including data privacy and security, device interoperability, and increased computing power requirements. At the same time, the development of edge computing technologies, increased transparency of algorithms, and optimization of energy consumption will help overcome these barriers.
Despite all the challenges, AIoT is still a promising technology that has the potential to transform critical industries and ways of doing business, making them more efficient, flexible, and responsive to user needs.




