IoT Trends for 2025 You Need to Know About
December 13, 2024The Internet of Things (IoT) seamlessly embeds intelligence in every facet of our lives, from smart homes identifying your needs to industrial machines forecasting failures before they happen. As we move into 2025, IoT technologies are developing at breathtaking speeds, changing industries and everyday life. Yet, there are problems associated with innovation – security, interoperability, and scalability are still major issues. IoT trends for 2025 are not limited to the state-of-the-art technology itself; they are targeted to tackle those problems and, at the same time, create the foundation for smarter, more interactive systems. So, what’s next for IoT? In this article, we’ll consider the top IoT trends in 2025 and figure out how they’ll impact businesses, consumers, and the world at large.
1. AI and machine learning integration
AI and ML are moving IoT devices from simple data-gatherers to intelligent decision-makers. Over the next year, AI-integrated IoT will work with massive amounts of real-time data generated by billions of devices to empower smarter automation and intelligent decision-making. This advancement is considered one of the most important trends associated with smart city applications. For example, AI in traffic management systems can detect traffic patterns and advise changes in traffic light patterns. Let’s consider an example. Due to advanced digital connectivity, Seoul is a global leader in smart city innovation. The city's extensive public Wi-Fi network covers all outdoor spaces. It ensures ubiquitous internet access, and Samsung's intelligent transportation systems optimize traffic flow using AI technology. With the self-optimizing ability of IoT ecosystems, problems related to data protection and algorithm robustness are being solved, which brings new opportunities for various fields.
2. Smart energy management
Energy management is one of the most critical components of IoT for smart buildings, and we have only scratched the surface of its potential. Today, only a small percentage of buildings have access to real-time energy reporting, and many still use obsolete manual meter readings. This gap creates a tremendous opportunity for IoT-powered solutions to change energy management. You can consider the Kaa end-to-end energy asset management solution. Property managers can use it to monitor energy usage levels in real-time through wireless submetering. For example, a hotel chain may use IoT to submeter guest rooms and other areas; this allows energy usage to be identified and energy-saving techniques to be targeted to specific regions. Access to organized, real-time smart energy metering data can help identify inefficiencies. For example, IoT sensors may disclose that a retail store's lighting consumes too much energy after hours or that a data center's cooling systems are overactive during low-usage periods. These insights enable organizations to quickly deploy solutions that drastically cut energy waste.
3. 5G-enabled IoT expansion
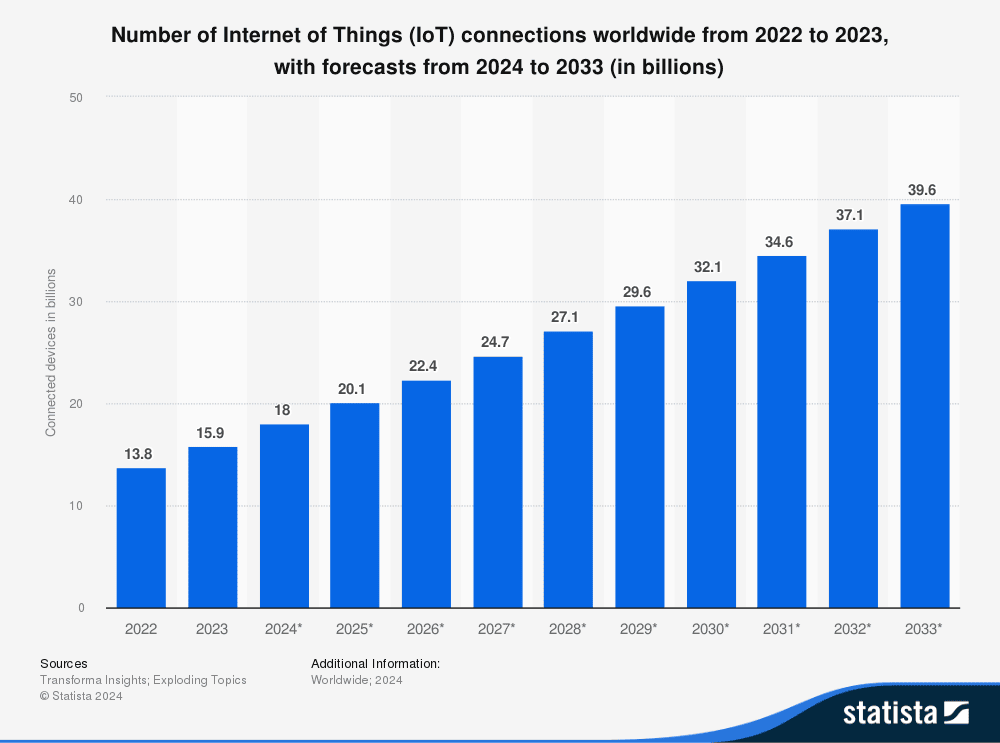
The deployment of 5G networks worldwide turbocharges the IoT sector, providing ultra-high-speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity. According to Statista, the number of IoT devices worldwide is forecast to almost double from 15.9 billion in 2023 to more than 32.1 billion IoT devices in 2030, and 5G will play a key role in enabling them. One transformative application is autonomous vehicles. 5G can provide near-instant communication between cars, traffic lights, and roadside sensors, enhancing safety and productivity. Manufacturing is also benefiting: wearable devices using 5G IoT bring about real-time monitoring and control. In healthcare, 5G allows remote surgeries via IoT-enabled robotics. Surgeons in various cities can now perform operations at the same time on patients placed with them, a process that wasn't previously possible with slower networks. Nevertheless, 5G technology also brings issues like high infrastructure costs and energy consumption. Still, its impact is undeniable. As the coverage increases, 5G will release IoT to its maximum benefits, creating a smart, faster-connected world where devices talk to each other continuously for better, faster operations.
4. Expediting IoT connectivity with edge computing
Edge computing is transforming the Internet of Things by bringing data processing closer to the source, thus lowering latency and bandwidth requirements. Spherical Insights predicts that the global edge computing market size is expected to reach USD 157.91 billion by 2030, thanks to its usage in IoT growth. Consider a factory with thousands of IoT sensors. Cloud-based systems have limitations for latency when processing that much data remotely. Edge computing allows for the processing of data locally, which allows for on-site decision-making. For example, Siemens applies edge IoT in factories for equipment monitoring and diagnosing problems in milliseconds, minimizing downtime by 20%. Another compelling use case is in autonomous drones. By localizing data processing, drones can make immediate navigation decisions, which is essential in time-sensitive applications like disaster response. Retail is also seeing a transformation. Amazon Go stores use edge computing to analyze shopper behavior in real-time, enabling cashier-less checkouts. The benefits extend beyond speed. Edge computing enhances data security by reducing reliance on centralized cloud systems, minimizing risks of breaches during transmission.
5. Sustainability and green IoT
According to the World Economic Forum, green IoT is a key driver of sustainability and is projected to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20% in the coming decades. Smart grids are a standout example. IoT-enabled grids optimize energy distribution by matching supply with demand, thus reducing energy waste. The U.S. Department of Energy states that smart grid systems have already reduced electricity outages by 50%, saving billions in operational costs. IoT in agriculture is also driving sustainability. Precision farming technologies like IoT soil sensors monitor moisture and nutrient levels; they minimize water and fertilizer use. Also, IoT smart waste management uses smart bins to track and optimize collection schedules - this approach significantly reduces fuel consumption in smart cities like Copenhagen. Green IoT devices themselves are also becoming more energy-efficient. Solar-powered IoT sensors, for instance, can operate in remote areas without traditional power sources.
6. Smart agriculture
IoT is transforming agriculture into a data-driven industry, expected to surpass $18.1 billion in market value by 2026, as described in the Markets and Markets research. IoT soil sensors, precision irrigation, and drone monitoring are already greatly increasing farm efficiency. Real-time data on soil, temperature, and humidity is collected by the IoT sensors so that farmers can take action accordingly. Since the data collected is real-time, and analysis is done on-site, the agriculture workers are able to observe emerging problems and mitigate crop loss. Livestock monitoring is another game-changer. IoT wearables track health metrics like heart rate and temperature and alert farmers to potential illnesses. Companies like Moocall have reduced livestock losses by 25% using such solutions. IoT also supports sustainable farming practices. Smart systems like hydroponics and vertical farming use IoT to regulate light, water, and nutrients. The result is enabled year-round cultivation with minimal resource usage.
Interesting: Discover how Kaa transforms farming operations with a smart farm management solution that provides real-time insights.
7. IoT in healthcare boom
The global IoT in the healthcare market is expected to experience significant growth, reaching USD 952.3 billion by 2032 (Accesswire). The Internet of Things has a wide range of applications in healthcare, from improving emergency response and reducing hospital stays to allowing research and more efficient resource planning. IoT gadgets in healthcare have numerous benefits, including more precise diagnosing and efficient care, more patient involvement, higher operational efficiency, cheaper operating expenses, and increased patient reach for hospitals. Among the various types of IoT medical devices are wearables such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, smart implants, remote patient monitoring devices, telemedicine kits, connected imaging machines, and even smart hospitals. However, there are still challenges like data privacy and device interoperability in healthcare. Despite this, IoT is empowering healthcare providers to offer better, faster, and more efficient care that saves lives and reduces costs.
8. IoT-blockchain synergy
IoT and blockchain are a powerful combination that addresses critical challenges like data security, transparency, and device authentication. Blockchain’s decentralized ledger ensures that IoT data remains tamper-proof. For example, in supply chain management, blockchain-backed IoT devices track products in real-time; it ensures authenticity and reduces fraud. IBM and Walmart’s Food Trust program uses this technology to trace produce and cut contamination response time from weeks to seconds. Blockchain also enhances IoT cybersecurity. Given that billions of devices are connected, it is essential to authenticate them. Projects like Helium Network use blockchain to manage IoT devices, which prevents unauthorized access securely. In healthcare, blockchain-IoT synergy enables secure patient record sharing and gives patients control and privacy over their data.
9. Interoperability standards take charge
The IoT ecosystem’s rapid expansion has led to a fragmented market where devices often fail to communicate. Organizations like the Connectivity Standards Alliance (formerly Zigbee Alliance) are leading the charge with protocols like Matter. Matter-certified devices can work across different brands. For instance, a smart home can use devices from Philips, Google, and Amazon without compatibility issues. In healthcare, interoperability is vital for patient care. IoT devices must share data across platforms like electronic health records (EHRs) to enable comprehensive care. Adopting standards like HL7’s FHIR improves interoperability in medical IoT systems and reduces diagnostic delays. Interoperability is also critical for smart cities. Traffic systems, energy grids, and public services rely on IoT devices working together. For example, Singapore is adopting open standards to integrate its IoT infrastructure; this solution improves operational efficiency.
Final words
Towards the close of 2025, the IoT landscape is set to redefine how we live, work, and interact with technology. IoT is no longer just a concept; this is an integral part of our future. AI-powered decision-making, sustainable innovations, and enhanced IoT connectivity technologies - these trends represent the incredible potential of IoT as well as the challenges we must overcome to benefit from its full power. The innovations discussed are not isolated, they’re converging to create a world that’s smarter, safer, and more connected. Adopting these trends will be critical to staying ahead in an IoT-driven world. Welcome to the IoT era, where things are intelligent, interconnected and are a matter of transforming influence.




